Hi, I’m Leo, a Network Engineer with over 10 years of experience in the field. Over the years, I’ve been through countless technical interviews, and one of the topics that always comes up in networking interviews is BGP (Border Gateway Protocol). Whether you’re interviewing for a mid-level networking role or a senior architect position, you can bet that questions about BGP will show up.
In this blog, I’m going to walk you through some of the most common BGP interview questions, explain why they’re asked, and provide detailed solutions and examples to help you ace them. Plus, I’ll share how tools like Ninjafy AI have been game-changers for me in preparing for these types of interviews.
Let’s dive in!
1. What is BGP, and Why is it Important?
Understanding the Basics
BGP, or Border Gateway Protocol, is the protocol that powers the internet. It’s used to exchange routing information between autonomous systems (ASes). Think of it as the system that decides the best path for your data to travel across the complex web of networks that make up the internet.
Common Interview Question:
“Can you explain BGP to someone who has no networking background?”
When answering this, simplify the concept:
“Imagine the internet as a giant map. BGP is like a GPS system that tells data packets the best route to take to reach their destination. It does this by exchanging routing information between networks, ensuring data flows smoothly and efficiently.”
2. How Does BGP Establish a Connection?
Sub-heading Opening Paragraph
Establishing a BGP session involves a series of steps, much like forming a relationship. It starts with identifying the neighbor, exchanging capabilities, and then maintaining the connection.
Dive Deeper:
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how BGP establishes a connection:
- Neighbor Discovery: BGP peers must be manually configured to recognize each other.
- TCP Connection: BGP uses TCP port 179 to establish a reliable connection.
- Open Message: Peers exchange their AS numbers, BGP version, and other parameters.
- Keepalive Messages: These are sent periodically to ensure the connection remains active.
Table: Key BGP Connection Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
| AS Number | Identifies an autonomous system | 65001 |
| Hold Time | Time before declaring a peer dead | 180 seconds |
| BGP Identifier | Unique identifier for the BGP router | 192.168.1.1 |
3. What Are the Different BGP States?
Sub-heading Snippet
BGP has multiple states during the establishment of a session. Understanding these is crucial for diagnosing connectivity issues.
Detailed Explanation of BGP States:
- Idle: The router is waiting to initiate a connection.
- Connect: The router is attempting to establish a TCP session.
- Active: If the connection fails, the router retries.
- OpenSent: The router sends an open message to its peer.
- OpenConfirm: The router waits for the peer’s acknowledgment.
- Established: The session is fully active, and routing updates are exchanged.
When asked about these states, remember to emphasize “Established” as the goal state.
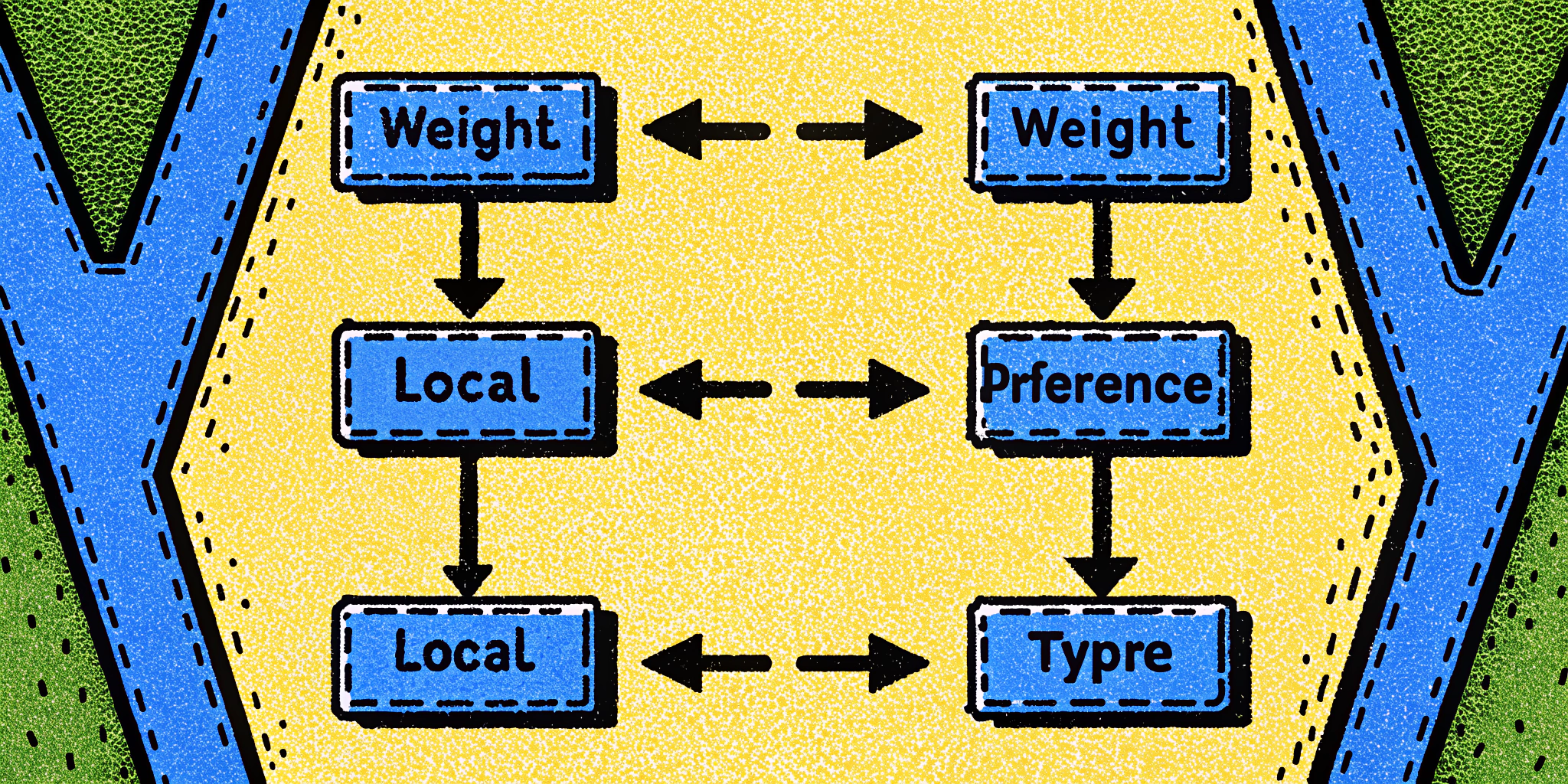
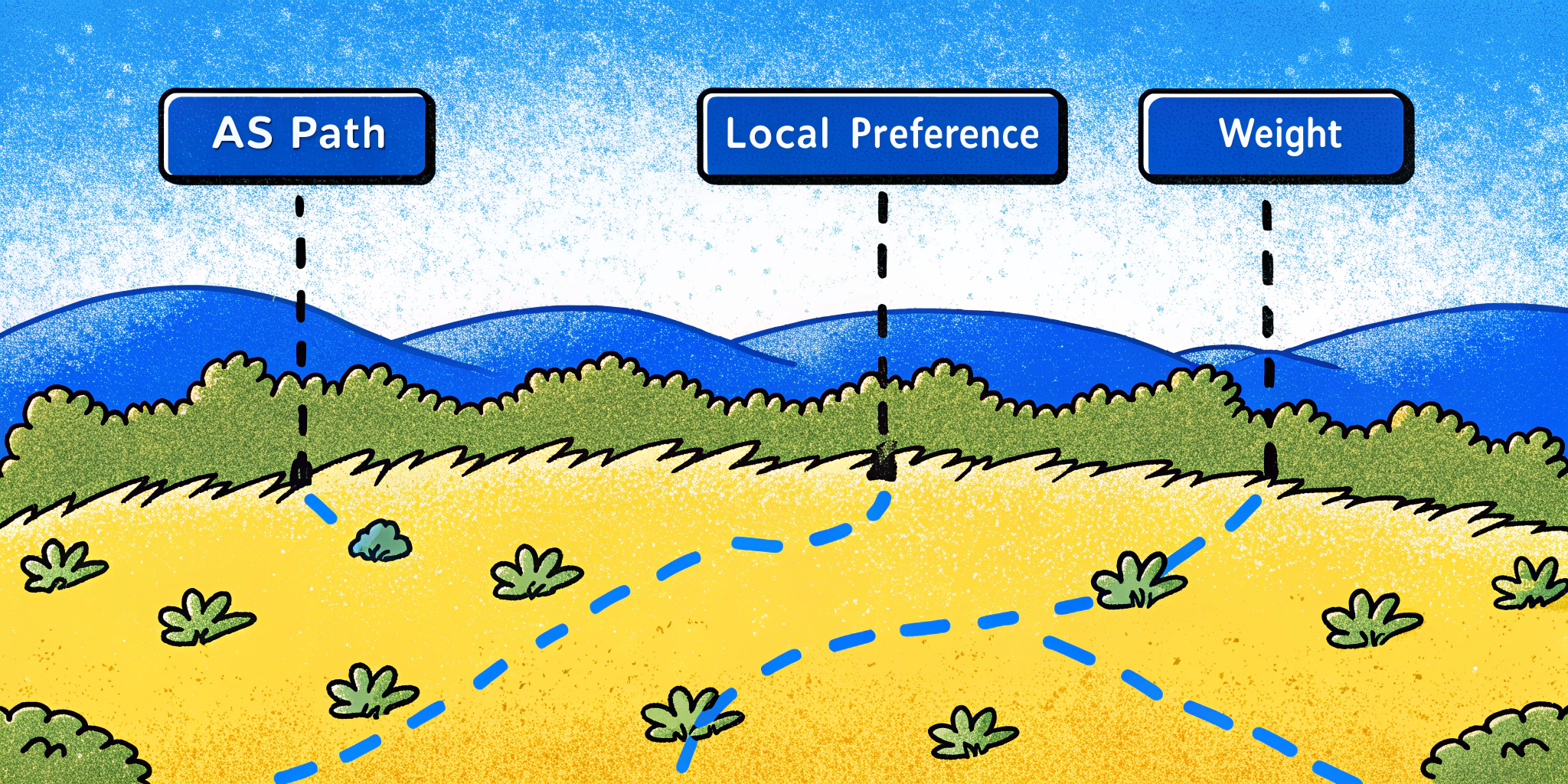
4. BGP Path Selection Process
Sub-heading Dive Deeper Paragraph
BGP uses several attributes to determine the best path for routing data. Here’s the order of priority:
- Weight: Highest weight wins (Cisco-specific).
- Local Preference: Higher value is preferred.
- AS Path: Shorter paths are preferred.
- Origin Type: IGP > EGP > Incomplete.
- MED (Metric): Lower values are preferred.
Table: BGP Path Selection Attributes
| Attribute | Description | Preference Logic |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Locally assigned value | Higher value preferred |
| Local Preference | Indicates preferred outbound path | Higher value preferred |
| AS Path | Number of AS hops | Shorter path preferred |
5. What is Route Aggregation in BGP?
Example Question:
“What is the purpose of route aggregation in BGP?”
Route aggregation reduces the size of routing tables by summarizing multiple routes into a single advertisement. For example:
- Instead of advertising
192.168.1.0/24,192.168.2.0/24, and192.168.3.0/24, you can advertise192.168.0.0/22.
This improves efficiency and reduces overhead.
6. Troubleshooting BGP Issues
Common Scenarios to Watch For:
- Neighbor Not Established: Check TCP port 179, AS numbers, and IP reachability.
- Routes Not Propagated: Verify route filters and prefix lists.
- Flapping Connections: Investigate unstable links or misconfigurations.
Using tools like Wireshark or router logs can help pinpoint issues.
7. Mock Interviews: The Ninjafy AI Advantage
When it comes to preparing for technical interviews, I can’t recommend Ninjafy AI enough. As an AI interview copilot, it helped me practice BGP scenarios with real-time feedback.
Here’s how I used it:
- Set up mock interviews to simulate real-world questions on BGP.
- Used the Industry Brain feature to focus on networking-specific challenges.
- Practiced with personalized models to refine my responses based on my actual resume.
The best part? It’s fully undetectable during live interviews, so you can stay confident and focused.
Conclusion: Ace Your BGP Interviews with Confidence
Mastering BGP interview questions doesn’t have to be daunting. By understanding the core concepts, practicing with real-world scenarios, and leveraging cutting-edge tools like Ninjafy AI, you can walk into your next interview with confidence.
Remember, preparation is key. Review the states, understand the attributes, and practice your troubleshooting skills. You’ve got this!